Efficient irrigation technologies are vital for sustainable agriculture, especially in regions facing water scarcity. By adopting modern and traditional water-saving methods, farmers can ensure better crop yields while conserving water resources. Below, we explore several innovative and effective irrigation techniques that contribute to sustainable farming practices.
Drip Irrigation: Minimizing Water Loss
Drip irrigation is a revolutionary method that delivers water directly to the roots of plants through a network of pipes, tubing, and emitters. This technique minimizes water loss due to evaporation or runoff and can save up to 80% of water compared to traditional methods. By providing water and nutrients precisely where they are needed, drip irrigation not only conserves water but also enhances crop productivity. Farmers can also customize the system to suit different crops and soil types, making it a versatile solution for various agricultural needs.
Real-Time Monitoring with Soil Moisture Sensors
Soil moisture sensors are an innovative tool that helps farmers monitor soil water levels in real-time. These devices provide accurate data on when and how much to irrigate, preventing both over-watering and under-watering. By ensuring that plants receive the right amount of water at the right time, soil moisture sensors promote healthier crop growth and reduce water wastage. Integrating these sensors with automated irrigation systems can further streamline water management on farms.
Enhancing Water Quality Through Enrichment
Water enrichment involves improving the quality and nutrient content of irrigation water. This ensures that plants receive the necessary minerals and nutrients for optimal growth. By enriching irrigation water, farmers can boost crop health and yields while reducing the need for additional fertilizers. This method also supports sustainable farming practices by minimizing nutrient runoff into surrounding ecosystems.
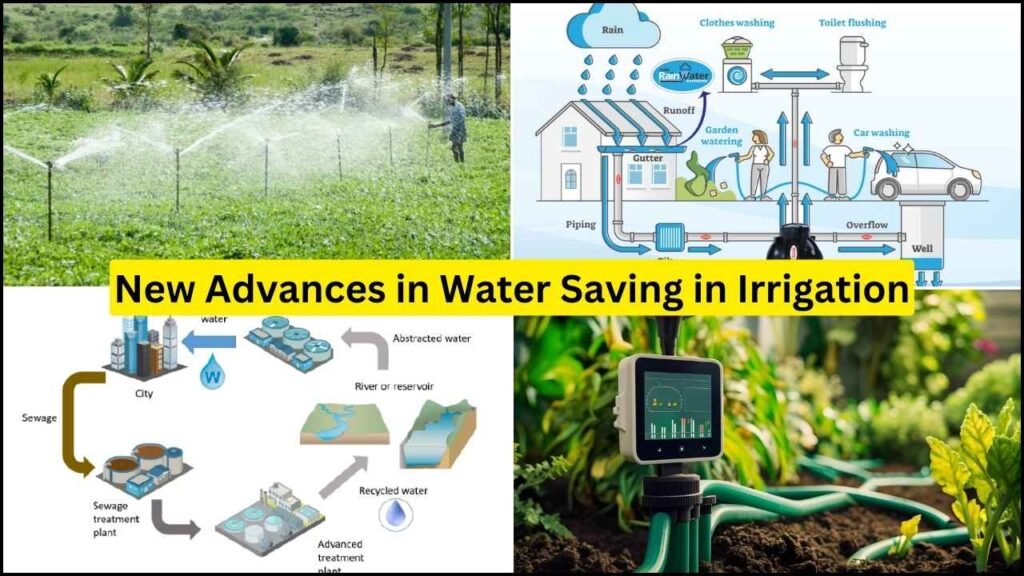
Rainwater Harvesting: A Traditional Approach with Modern Benefits
Rainwater harvesting is a time-tested technique that involves collecting and storing rainwater for future use. Modern rainwater harvesting systems include components such as gutters, downspouts, filters, and storage tanks. This method not only provides a supplementary water source for irrigation but also helps reduce dependence on groundwater and municipal water supplies. In regions with erratic rainfall patterns, rainwater harvesting can be a reliable solution for meeting agricultural water needs.
Crop Rotation for Improved Water Efficiency
Crop rotation is a simple yet effective practice that involves alternating the types of crops grown in a specific area. By choosing water-efficient crops and improving soil quality, farmers can reduce the need for frequent irrigation. This practice also enhances soil structure and fertility, allowing it to retain moisture more effectively. Crop rotation thus contributes to water conservation while supporting long-term soil health.
Mulching: Retaining Soil Moisture
Mulching is another practical technique for conserving water in agriculture. By covering the soil with organic materials such as straw, leaves, or compost, mulching reduces evaporation and helps retain soil moisture. Additionally, mulch regulates soil temperature, suppresses weeds, and adds organic matter to the soil as it decomposes. This simple yet effective practice can significantly reduce the amount of water needed for irrigation.
Smart Irrigation Systems: Precision Watering
Smart irrigation systems use data-driven tools and technologies to optimize water use. These systems rely on inputs such as weather forecasts, soil moisture data, and crop requirements to determine the ideal irrigation schedule. Automated sprinklers and drip systems can then deliver water precisely when and where it is needed. Smart irrigation not only conserves water but also reduces labor and energy costs, making it an ideal choice for modern farming.
Recycling Water for Irrigation
Water recycling involves treating and reusing wastewater for agricultural purposes. Treated wastewater can be a reliable source of irrigation water, especially in regions facing acute water scarcity. By recycling water, farmers can reduce their dependence on freshwater resources and contribute to sustainable water management. This practice also helps in managing wastewater disposal, minimizing its environmental impact.
Conclusion
Adopting advanced irrigation technologies is no longer a choice but a necessity for sustainable agriculture. Techniques like drip irrigation, soil moisture sensors, and rainwater harvesting offer practical solutions to conserve water while ensuring high crop yields. Practices such as mulching, crop rotation, and water recycling further enhance water use efficiency in agriculture.
Integrating these techniques with modern technology can help farmers make informed decisions and optimize their water management practices. Governments and agricultural organizations must also contribute by providing training, subsidies, and access to these technologies. Together, these efforts can pave the way for a more sustainable and water-efficient future in agriculture.
Efficient irrigation is not just about saving water; it’s about ensuring the long-term viability of farming and protecting our planet’s precious resources. By embracing these advances, we can achieve a balance between agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
FAQs
Q1: What is water recycling in irrigation?
Ans: Water recycling in irrigation involves reusing treated wastewater for crop irrigation, helping conserve fresh water.
Q2: What is smart irrigation?
Ans: Smart irrigation uses sensors, weather data, and automation to efficiently manage water use in irrigation systems, minimizing waste.